NFT has been around for some time, but it gained a lot of popularity in 2020, especially in the world of digital art. While NFTs have generated a lot of excitement, they have also been subject to criticism for their volatility, speculative nature, and susceptibility to fraudulent activities. This article by CoinMinutes aims to provide a clear and concise understanding of NFTs in just a few minutes.
What Is an NFT?
An NFT or a Non-Fungible Token is a unique cryptographic token on the blockchain that represents a single asset. An asset is considered non-fungible when it is irreplaceable, like the famous “Mona Lisa” painting or Lady Gaga’s Beef Jacket. As they are one-of-a-kind objects, they hold a high value.
A Non-Fungible Token can be anything digitally related, such as music, artwork, video, cards, in-game items, and so on. They can be traded online with real money or most commonly, with cryptocurrency and even with another NFT themselves.
Why Does NFT Have Value?
Similar to an in-person work of art, the value of a Non-Fungible Token is determined by various factors, such as the rarity of the NFT, its popularity, originality, demand on the market, and most importantly, the buyer’s perception of its worth. People may value an NFT due to its artistic and cultural significance, or simply because they wish to support the creator.
The value of NFTs currently lies in three main aspects:
- Scarcity: NFTs are often created in limited quantities or as one-of-a-kind digital assets. This scarcity mimics the rarity found in traditional art or collectibles, making them inherently valuable to collectors.
- Ownership and Authenticity: NFTs are backed by blockchain technology, providing a transparent and immutable record of ownership. This digital provenance assures buyers that they own the original and authentic version of a digital asset, which is a critical factor in establishing value.
- Community and Culture: NFTs have become a cultural phenomenon, with communities forming around specific artists, projects, or platforms. The sense of belonging and shared enthusiasm contribute to the perceived value of NFTs within these communities.
History of NFT
Non-Fungible Tokens have been around for quite some time, not just as a recent trend. The very first NFT, named “Quantum” and created by Kevin McKoy in 2014, was initially tokenized on the Namecoin blockchain. However, it gained widespread attention and was eventually sold on Ethereum in 2021.
Now, the technical side of Non-Fungible Tokens involves standards like ERC-721 and ERC-1155. The ERC-721 standard, developed on Ethereum, defines the rules for transferring ownership, confirming transactions, and ensuring secure transfers in applications. ERC-1155, introduced six months later, takes it up a notch by consolidating multiple Non-Fungible Tokens into a single contract, making transactions more cost-effective.
How Does NFT Work?
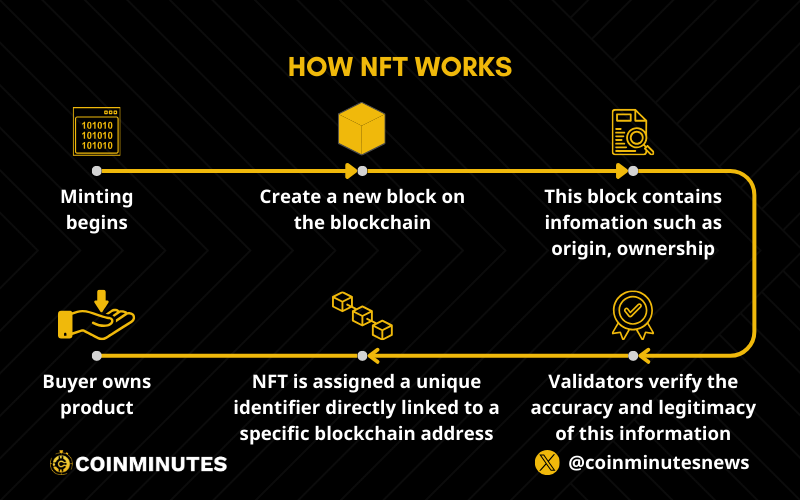
The process of creating a Non-Fungible Token is known as minting, and it involves leveraging blockchain technology, typically on platforms like Ethereum.
Minting begins with the creation of a new block on the blockchain. This block serves as a container for information about the NFTs being minted. The information includes details about the digital asset, such as its origin, ownership, and any other relevant metadata. Validators on the blockchain network verify the accuracy and legitimacy of this information before the block is officially closed.
Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, play a crucial role in the minting process. They automate the tasks of assigning ownership and managing the transferability of the Non-Fungible Token. This ensures that the NFT operates according to predefined rules, such as determining who can buy, sell, or transfer the digital asset.
Once an NFT is minted, it is assigned a unique identifier directly linked to a specific blockchain address. This identifier distinguishes it from any other token on the network. Each token has an owner, and this ownership information, including the blockchain address where the token resides, is publicly accessible.
This transparency and immutability of blockchain ensure that the ownership and transaction history of each Non-Fungible Token can be easily traced and verified. The uniqueness and scarcity of NFTs, combined with the security and transparency of blockchain technology, contribute to the value and appeal of these digital assets in the growing world of digital ownership and collectibles.
How Is an NFT Different from Cryptocurrency?
Non-Fungible Token is a bit of a departure from your typical cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. While those currencies are interchangeable and always hold the same value, NFTs play by different rules.
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency | Non-Fungible Tokens |
|---|---|---|
| Fungibility | Fungible: Units are interchangeable and have the same value (e.g., Bitcoin). | Non-Fungible: Each token is unique and cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis with another NFT. |
| Use Case | Medium of exchange, store of value, unit of account. Commonly used for transactions and investments. | Represents ownership or proof of authenticity for specific digital or physical assets (e.g., digital art, music, videos). |
| Interchangeability | Units can be traded on a like-for-like basis. (One Bitcoin equals another Bitcoin.) | Each NFT is distinct and cannot be swapped on a direct basis with another NFT. Individual characteristics make them unique. |
| Standardization | Follows standards like ERC-20 (for tokens on Ethereum) or similar protocols for interoperability. | Follows standards like ERC-721 or ERC-1155, specifying how these unique tokens should be created, owned, and transferred. |
| Primary Function | Medium of exchange, digital currency. | Represents ownership, authenticity, or proof of a unique digital or physical asset. |
| Examples | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin. | Cryptokitties, NBA Top Shot, digital art pieces. |
How to Buy NFT?
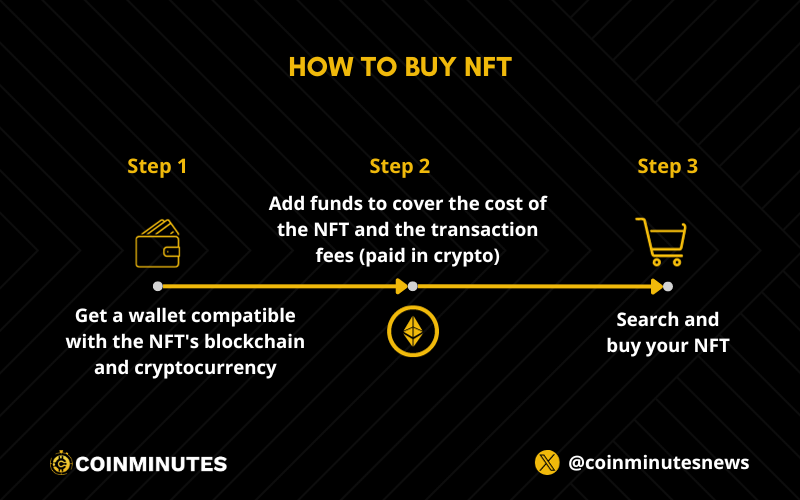
Non-Fungible Tokens are easily bought and sold on various digital marketplaces such as OpenSea, SuperRare, Rarible, Binance NFT, and many others. To purchase an NFT, you will need a digital wallet that supports the blockchain and the cryptocurrency that the NFT is based on. For instance, if you wish to buy a Non-Fungible Token on Ethereum, you must have a wallet that supports Ethereum and Ether (ETH). Additionally, you will require sufficient funds in your wallet to cover the cost of the NFT and the transaction fees, which are also paid in cryptocurrency.
Once you have a wallet, you can browse or search for NFTs on various platforms and marketplaces that offer them. You can filter or sort the NFTs by category, price, popularity, or other criteria. You can also view the details and history of each Non-Fungible Token, such as the creator, owner, description, metadata, and transactions.
When you find a Non-Fungible Token that you like, you can either buy it directly at a fixed price or bid on it in an auction. You can also make an offer to the seller if they accept it. To complete the purchase, you need to confirm the transaction and sign it with your wallet. The transaction will then be processed by the blockchain network and recorded in the ledger. Finally, the NFT will be transferred to your wallet and you will become the new owner of it.
Is NFT Safe?
Even though Non-Fungible Tokenis still new and there are already some rumors around them about legal uncertainty and market volatility, they are generally safe as long as you follow some basic precautions and best practices when buying or creating them, including:
- Do Your Research: Before buying or creating a Non-Fungible Token, make sure you understand the risks and benefits involved. You should also verify the authenticity and reputation of the platform, marketplace, creator, or seller that you are dealing with. You can check their reviews, ratings, feedback, social media presence, or other sources of information.
- Use a Secure Wallet: Choose a wallet that is compatible with the blockchain and the cryptocurrency that you are using for your Non-Fungible Token transactions, especially with a high level of security and privacy features. You should also keep your wallet updated and avoid using public or shared devices or networks to access it
- Protect Your Keys: Your private keys are the codes that allow you to access and control your wallet and your NFTs. You should never share your keys with anyone or store them online or in plain text. You should also use a hardware wallet or a cold storage device to store your keys offline and away from hackers or malware.
- Be Careful with Links: When browsing or clicking on links related to Non-Fungible Tokens, make sure they are legitimate and trustworthy. You should avoid phishing links that may try to trick you into giving away your personal or financial information or downloading malicious software. You should also use a secure browser and antivirus software to protect yourself from malware or viruses
Can NFT Be Hacked?
Non-Fungible tokens are normally inside highly secured environments and resistant to hacking because they are stored on a decentralized network of computers that use cryptography and consensus mechanisms to validate and record transactions. This makes it very difficult for anyone to tamper with or alter the data on the blockchain without being detected or rejected by the network.
However, there are still some potential ways that Non-Fungible Tokens can be hacked or compromised, such as:
- Flatform Bugs: Some NFTs may have smart contracts embedded in them that enable them to have dynamic or interactive features. However, if these smart contracts have coding errors or vulnerabilities, they may be exploited by hackers to manipulate or steal the Non-Fungible Tokens or the funds associated with them.
- Platform Breaches: Some platforms or marketplaces that host or sell NFTs may not have adequate security measures to protect their users’ data or assets. They may be hacked by cybercriminals who can access their databases, servers, or wallets and steal or damage the Non-Fungible Token or the funds stored on them.
- User Errors: It’s common for users to make mistakes or be careless when handling their NFTs. Losing their keys, forgetting passwords, sending NFTs to the wrong address, falling for phishing scams, or downloading malicious software can result in the loss of access or ownership to their NFT. Therefore, it’s crucial to be cautious and take necessary precautions to safeguard NFTs and wallets.
OpenSea, one of the biggest Non-Fungible Token marketplaces, warned customers about email phishing attacks in 2023. The attacks happened due to a major data breach by a staff member of the platform. Even though security action had been taken, this incident impacted thousands of people who had linked their email with OpenSea.
Correct- there is no smart contract vuln. But unfortunately for @opensea I just received a phishing attempt, to an email that was strictly dedicated to my OpenSea API key. In other words, dev contacts have been exfiltrated from OpenSea and are the real target in this campaign https://t.co/GD4UgwWIrx pic.twitter.com/rtyUJBMlwl
— Quantity (@quantity) November 13, 2023
How to Make Money with NFT?
Making money with Non-Fungible Tokens involves various strategies and activities within the Non-Fungible Token ecosystem. Here are some common ways:
- Create and Sell NFTs: If you’re an artist, musician, or creator, you can create digital content and tokenize it into a Non-Fungible Token. You can then sell these NFTs on platforms like Opensea, Rarible, or Mintable.
- Invest in NFTs: Purchase NFTs that you believe will increase in value over time. Some people treat Non-Fungible Tokens as investments, hoping their value will be appreciated, and they can sell them for a profit later.
- Play-to-Earn Games: Engage in Play-to-Earn games like Axie Infinity, where players can earn cryptocurrency or NFTs by playing the game. This involves an initial investment in-game assets.
- NFT Staking: Some platforms allow you to stake NFTs, earning rewards or additional tokens over time.
- NFT Airdrops: Participate in Non-Fungible Token airdrops where projects distribute free NFTs to holders of specific tokens or participants in their community.
Conclusion
Non-Fungible Tokens are a new and exciting phenomenon, opening up many opportunities for creators, collectors, and investors. However, they also come with some challenges and risks that need to be understood and addressed. To conclude, NFTs are not for everyone, but they may be for you if you are interested in exploring the possibilities and potentials of this emerging technology.







