Ethereum is a popular blockchain technology platform in the virtual currency market that often gets talked about. If you want to know what Ethereum is and understand its advantages and disadvantages, then read this article by CoinMinutes.
What Is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain network that enables developers to build and deploy smart contracts and DApps without the interference of intermediaries. That has acquired immense popularity and recognition in cryptocurrency and distributed registry technologies.

Key Features of Ethereum
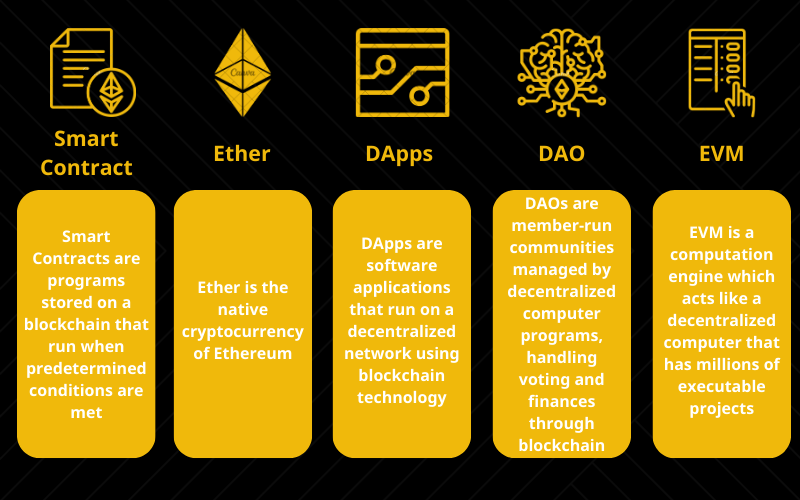
Smart contracts
Ethereum stands out due to its utilization of smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements programmed with predefined rules and conditions. The execution of these contracts occurs automatically upon the fulfillment of specific conditions. This unique feature opens up a wide range of possibilities, including crowdfunding, decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and many other applications.
Ether (ETH)
Ether is the second most valuable and significant unit in the world of digital currencies after Bitcoin. Ether is not only a cryptocurrency, but also a crucial element in the Ethereum ecosystem, which is one of the most popular and diverse blockchain platforms in the industry.
Ether is utilized as a payment method for transactions on Ethereum, which facilitates the execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). Developers can create complex applications without relying on traditional intermediaries, which leads to cost savings and enhanced transparency in transactions.
DApps (Decentralized Applications)
DApps, which are short for Decentralized Applications, are software applications that run on a decentralized network using blockchain technology. Ethereum, a blockchain platform that is known for its flexibility and programmability, is the core of this innovation. DApps can be created and deployed on Ethereum without the need for a central authority, making them secure, transparent, and resistant to censorship.
Ethereum serves as the basis for building and managing these DApps, providing a decentralized infrastructure that ensures data integrity and enables the execution of smart contracts. These smart contracts are self-performing agreements with predefined conditions, automating processes and eliminating the need for intermediaries, thereby promoting a reliable and efficient environment for various applications.
DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization)
A Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) is a concept that is related to blockchain technology and cryptocurrency. A DAO is an automated system that operates without requiring central control. Smart contracts are used to execute and manage activities, to ensure transparency, fairness, and inclusive participation for all members without relying on intermediaries.
Decisions within a DAO are usually based on decentralized principles, using input and voting from its members or users. To manage projects, make decisions about the distribution of digital assets, or carry out various activities that require community consensus, DAOs can be employed.
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
The Ethereum virtual machine (EVM) is a crucial pillar in the Ethereum ecosystem. The EVM automates predefined tasks and operations based on specified conditions by enabling smart contracts coded in languages like Solidity. Verification and execution of transactions and smart contracts can be facilitated by every node in the Ethereum network running an instance of the EVM.
Executing smart contracts on the EVM results in a fee called ‘gas’, which compensates for the computational work and network resources consumed. Gas fees are charged to users when they engage in transactions or interact with smart contracts, and they can vary depending on network conditions and the complexity of activities performed.
How Ethereum Works
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, a distributed and immutable ledger that records all transactions and data across a network of decentralized computers, known as nodes, is the heart of Ethereum’s functionality. The Ethereum blockchain has a list of transactions that are linked together using cryptographic hashes to ensure the security and integrity of the entire system.
The Ethereum blockchain is decentralized and resistant to single points of failure or censorship because it is not controlled by any central authority. By using this characteristic, a trustless and transparent environment can be created where participants can interact directly with each other without the need for intermediaries.
Proof-of-Work (PoW) Mechanism
To validate and add new blocks to the blockchain, Ethereum initially employed a consensus mechanism called Proof-of-Work (PoW). Miners compete in this process to solve complex mathematical puzzles, and the first one to find the correct solution is granted the right to add a new block. The mining process is both secure and energy-intensive, as it requires significant computational power.
Miners are rewarded with Ether – the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain, for their efforts in securing the network and processing transactions. Participating in the network and maintaining its integrity is incentivized by this.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Mechanism
Proof of stake (PoS) is Ethereum’s consensus mechanism. It was implemented to replace the previous Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. PoS is built based on validators having to stake some amount of ETH in a smart contract on Ethereum. If a validator tries to cheat the network (such as proposing multiple blocks when they should send one or sending conflicting certificates), a portion or all of their staked ETH may be destroyed.
To participate as a validator, users must deposit 32 ETH into the deposit contract and run three separate software: an execution client, a consensus client, and a validation client.
Pros and Cons of Ethereum
Pros of Ethereum
- Smart Contract Functionality: One of the key features that sets Ethereum apart from other cryptocurrencies is its ability to execute smart contracts. These contracts allow for credible transactions to be facilitated, verified, and enforced without the need for intermediaries. By utilizing Ethereum’s smart contract functionality, it is possible to create a wide range of applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols and decentralized applications (DApps). This feature allows for transparent and trustless interactions, which has sparked innovation and revolutionized various industries.
- Decentralization: Ethereum is a decentralized platform that operates on a global network of nodes to validate and record transactions on its blockchain. Unlike traditional centralized systems, Ethereum does not rely on any single point of failure or control. This decentralized approach makes it more secure and resistant to censorship, ensuring that no single entity or government can manipulate or control the network. The platform’s decentralized nature also provides individuals with full ownership and control of their digital assets and interactions.
- Wide Adoption: Ethereum has gained remarkable adoption and community support since its inception. Its ecosystem is robust and hosts a wide range of projects, from small-scale startups to large enterprises. Ethereum’s flexibility and powerful capabilities have led developers and entrepreneurs worldwide to embrace it. Decentralized applications built on Ethereum have attracted users from various sectors, including finance, gaming, supply chain management, and healthcare.
- Upgradability: Another important benefit of Ethereum is its ability to evolve and adjust over time. Ethereum is not a static protocol; it has been the object of several updates and improvements since its launch. Such a critical upgrade is the transition from a working proof (PoW) to a participating proof (PoS) consensus mechanism, known as Ethereum 2.0. This upgrade aims to address scalability issues, reduce energy consumption, and increase transaction throughput. The upgradability of Ethereum ensures that it remains a cutting-edge platform that can meet the demands of a rapidly evolving blockchain landscape.
Cons of Ethereum
- Energy Consumption: One of the major concerns associated with Ethereum is its energy consumption. The Ethereum network relies on a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which necessitates a significant amount of computational power to verify transactions and secure the network. Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles, resulting in a substantial consumption of electricity. Ethereum’s high energy consumption has caused environmental concerns and led to debates about the sustainability of blockchain technology.
- Security: Security is a critical aspect of any blockchain network, and Ethereum is no exception. Although the platform’s code is open-source and peer-reviewed, it is not immune to security vulnerabilities and exploits. Various security incidents have occurred in Ethereum in the past, such as smart contract bugs and attacks on decentralized applications. Smart contract vulnerabilities, such as reentrancy bugs and integer overflow, can cause the platform to lose funds or be manipulated.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The decentralized nature of Ethereum has given rise to questions about its legal and regulatory status. Different countries have diverse approaches to cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, resulting in a patchwork of regulations that can create uncertainty for users and developers. Investor confidence, business operations, and the overall growth of the Ethereum ecosystem are all affected by regulatory uncertainty.
- Competitive Threats: Ethereum has faced increasing competition from other blockchain platforms, even though it was the first to introduce smart contracts and DApps on a large scale. Binance Smart Chain, Polkadot, and Solana are some of the alternative networks that offer different features and advantages that appeal to developers and users alike.
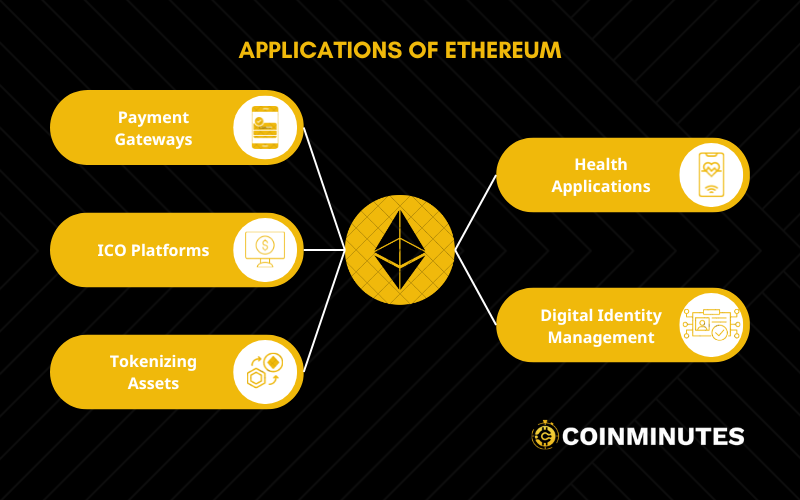
Applications of Ethereum
Payment Gateways
The field of payment gateways has seen some of Ethereum’s earliest and most well-known implementations. Ether (ETH), the native money of Ethereum, is used for both storing value and enabling decentralized transactions.
Through the use of trustless payment gateways developed on the Ethereum platform, businesses and people can send and receive money without using conventional middlemen like banks. Faster international transactions, lower fees, and greater financial inclusion have resulted from this, especially in areas with limited access to conventional banking services.
ICO Platforms
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) have made it possible for entrepreneurs to issue their digital tokens on the Ethereum blockchain and generate capital in a novel way. Without the aid of conventional venture capital firms, businesses might reach worldwide pools of investors through ICOs.
The idea of crowdsourcing and tokenized fundraising remains a prominent application of Ethereum’s smart contract capabilities, even though ICOs have encountered regulatory challenges and transformed into more regulated forms like Security Token Offerings (STOs) or Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs).
Tokenizing Assets
The creation of fungible and non-fungible tokens on Ethereum has made it possible to tokenize physical goods. Real estate, works of art, and other tangible goods can be tokenized to be represented on the blockchain as digital tokens.
Through this procedure, fractional ownership is made possible, liquidity is improved, and ownership transfers are made easier. By purchasing fractions of high-value assets, investors may now diversify their portfolios with ease, democratizing access formerly exclusive to the wealthy.
Health Applications
Ethereum and other blockchain technologies can completely change the healthcare sector. Ethereum-based apps can preserve patient privacy and facilitate interoperability across various healthcare providers by offering a secure and immutable ledger for health data. This might result in more thorough and accurate medical histories, fewer medical mistakes, and better research prospects.
Digital Identity Management
The self-sovereign identification concept of Ethereum enables anyone to own and manage their data. Without relying on a centralized authority, secure and verifiable identity verification is made possible via decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and verifiable credentials. Applications for this range from easing KYC procedures for financial services to secure online authentication and access management.
Payment gateways, ICO platforms, asset tokenization, health applications, and digital identity management are just a few examples of the innovative ways Ethereum is reshaping industries and driving forward the adoption of decentralized technologies. As Ethereum continues to evolve, its impact on various sectors is likely to expand even further, unlocking new opportunities and challenges along the way.
Ethereum Token Standard
Ethereum Token Standards encompass a set of rules and protocols defined within the Ethereum blockchain ecosystem to manage and represent various types of assets in the form of tokens, ranging from points and currencies to digital assets and more. The compatibility between different applications and services that use tokens on the same blockchain is ensured by these standards.
There are some popular Ethereum token standards:
- ERC-20: The most widely used token standard on Ethereum is called ERC-20 (Ethereum Request for Comments 20). It is frequently used to generate standard tokens like virtual currencies, points of loyalty, and ownership rights in non-financial applications. With the use of a standardized protocol, ERC-20 defines core operations for tasks like token transfers, balance checks, and communicating with contracts.
- ERC-721: This non-fungible token standard, known as ERC-721 (Ethereum Request for Comments 721), is frequently used to represent special and non-transferable assets. Tokens that represent in-game items, digital land rights, works of art, and other things are classic examples. Each ERC-721 token has a distinctive identification that is impossible to copy or replace.
- ERC-777: ERC-777 is a token standard for the Ethereum network that provides many improvements over the current ERC-20 standard, including brackets, clarity around decimals, and backward compatibility with ERC-20. However, it is difficult to implement properly and is vulnerable to various forms of attacks, so it is recommended to use ERC-20 as an alternative.
- ERC-1155: ERC-1155 is a digital token standard that Enjin created to create assets that are both Fungible (currency) and Non-Fungible (digital tokens, pets, and game items) on the Ethereum network. The ERC-1155 token standard permits users to transfer multiple tokens to the same wallet address during a single transaction. Users can save time and money by using this method instead of sending tokens individually.
- ERC-4626: The ERC-4626 standard, which was created by Joey-Santoro and two other colleagues at Fei Protocol, is used to develop yield-bearing tokens. Like other standards, ERC-4626 (Tokenized Vault Standard) was born to provide a framework for the development of Yield-token, helping the developing platforms of Yield-bearing tokens such as Aave (aToken), Yearn (yTokens)… have their Yield-bearing token standardization developed.
What Is Ethereum 2.0?
In 2022, Ethereum underwent a significant transformation with the implementation of Ethereum 2.0, transitioning its blockchain from a proof-of-work consensus mechanism to proof of stake. This revolutionary shift eliminated the necessity for miners, traditionally engaged in resource-intensive validation processes using costly crypto-mining equipment, and substantially reduced energy consumption.
Staking, a process wherein users lock a specific amount of cryptocurrency to engage in transaction verification, supplanted mining as the method for validating Ethereum transactions. The adoption of Ethereum 2.0 resulted in a remarkable reduction of the cryptocurrency’s carbon footprint, slashing it by an impressive 99.9%.
Bitcoin and Ethereum: Similarities and Differences
Similarities
- Blockchain Technology: Both Bitcoin and Ethereum utilize blockchain technology to record and verify transactions. The security and transparency of these blockchains are enhanced through decentralized and distributed ledgers.
- Cryptocurrency: Both are popular cryptocurrencies; Bitcoin (BTC) and Ether (ETH) are used for various transactions, investments, and value transfers within their respective networks.
- Limited Supply: Both Bitcoin and Ethereum have a predetermined supply limit. Bitcoin’s supply is limited to 21 million coins, while Ethereum is moving towards a proof-of-stake consensus, which will likely result in a more controlled issuance rate.
Differences
- Purpose and Functionality: Bitcoin primarily serves as a digital store of value and a medium of exchange. Ethereum is a platform that is designed to build decentralized applications (DApps) and execute smart contracts. In a nutshell, Ethereum is a store of products in diverse fields, while Bitcoin is just a currency for transactions.
- Smart Contracts and DApps: Ethereum introduced the concept of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with automated terms and conditions. The creation of decentralized applications that can execute code and manage assets without intermediaries is made possible by this.
- Consensus Mechanism: Bitcoin uses proof-of-work (PoW) as its consensus mechanism while Ethereum is transitioning from PoW to proof-of-stake (PoS) to improve scalability and energy efficiency.
- Development Community: Ethereum has a more active and versatile development community due to its focus on smart contracts and DApps.
How to Buy Ethereum?
It’s a prevalent misconception among individuals new to the Ethereum network: you don’t directly purchase Ethereum itself; rather, you acquire Ether, the native cryptocurrency utilized on the Ethereum network. Acquiring Ether on the Ethereum network is a straightforward process due to its widespread popularity:
Step 1: Select a Cryptocurrency Exchange
- Choose from reputable cryptocurrency exchanges and trading platforms like Coinbase, Binance.US, or Kraken.
- Alternatively, if you’re interested in acquiring common coins like Ether and Bitcoin exclusively, online brokerages such as Robinhood or SoFi are viable options.
- Be aware of trading or processing fees, which are commonly applicable across platforms.
Step 2: Deposit Fiat Money
- Fund your trading platform by depositing fiat currency, such as dollars.
- Link your bank account or debit card to facilitate the funding of Ether purchases.
Step 3: Purchase Ether
- Once your account is funded, use the deposited money to buy Ether at the prevailing Ethereum market price, alongside other available assets.
- Following the acquisition, you have the flexibility to hold, sell, or trade Ether for other cryptocurrencies in the future. Keep in mind the potential tax implications associated with selling or trading cryptocurrencies.
Step 4: Utilize a Wallet
- While your trading platform may provide a default digital wallet, relying solely on it poses security risks.
- Consider transferring coins earmarked for long-term holding into a separate digital wallet or a cold wallet, disconnected from the internet for enhanced security.
- This precautionary step mitigates the risk of coin theft in the event of an exchange hack.
Navigating the process of buying and securing Ether involves selecting the right platform, managing fiat deposits, making informed purchases, and prioritizing security through the use of reputable wallets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ethereum used for?
Ethereum is a platform that allows anyone to create secure digital technologies. Its native cryptocurrency is called Ether (ETH). The purpose of ether is to pay for work done supporting the blockchain, but it can also be used to pay for tangible goods and services if accepted by the seller.
Why is Ethereum so popular?
Ethereum has gained tremendous popularity and is still growing due to several reasons. One of the key factors that sets Ethereum apart from Bitcoin is its programmable blockchain. This means that Ethereum’s software network allows users to create and operate new tools, applications, DeFi, smart contracts, and NFTs.
Does Ethereum have a better future than Bitcoin?
Ethereum is gaining popularity among large institutions due to its flexibility and scalability. While Bitcoin is often referred to as “digital gold,” Ethereum is more like “digital oil” because it has a wider range of practical applications. In the long term, Ethereum will likely become the more valuable cryptocurrency because of its increasing practical use cases.
Conclusion
CoinMinutes has helped you understand what Ethereum is and its related features and terms. In summary, Ethereum is a groundbreaking platform in the cryptocurrency industry that offers more than just a digital currency.
Developers have been able to create decentralized applications that challenge traditional financial systems, enable peer-to-peer transactions, and introduce innovative concepts such as decentralized governance, ushering in a wave of innovation. Despite facing competition from newer blockchains, Ethereum’s strong developer community, established ecosystem, and recognition as a pioneer ensure its continued influence in shaping the future of blockchain technology and its applications.






