The term “Market Maker” is commonly used in the cryptocurrency industry, playing a crucial role in enhancing market liquidity and stability. But what is a Market Maker, and how does it function? Join us in exploring these concepts through the following article on Coinminutex.
What Is a Market Maker?
A Market Maker (MM) refers to the entity or individual within a cryptocurrency exchange responsible for offering trading and liquidity creation services. The primary role of a Market Maker is to ensure a constant availability of buyers and sellers for various financial instruments such as stocks, securities, coins, currencies, and other derivative products.
Market Makers actively engage in transactions by acting as both buyers and sellers of assets. Simultaneously, they stand ready to assist investors by facilitating the purchase or sale of assets as needed.
In essence, the Market Maker significantly contributes to fostering favorable conditions for seamless transactions in the market. Their presence enhances market liquidity, simplifying the trading process for investors.
How Does Market Maker Work?
Market makers function by presenting two distinct prices simultaneously: a lower buying price and a higher selling price for every asset. When investors wish to sell an asset, they do so to the market maker at a slightly reduced buying price compared to the prevailing market rate. Conversely, when they intend to buy, they acquire the asset at a slightly elevated price compared to the market value.
How Does Market Maker Earn Profit?
A Market Maker generates income by capitalizing on the difference between the Bid price (the price a buyer is willing to pay) and the Ask price (the price a seller is asking for). This disparity is commonly referred to as the “Spread” and is essentially the profit margin for the Market Maker. This practice is known as the market maker’s spread or bid-ask spread.
In simpler terms, the Market Maker’s method of earning profits is akin to a “trigger,” but on a larger and more sophisticated scale. This approach is also recognized as the Order Book.
Additionally, the Market Maker levies a transaction fee for each trade executed by a customer. For instance, platforms like Binance impose a fee of 0.1%, while FTX varies its fees between 0.02% and 0.07% based on the overall trading volume of customers.
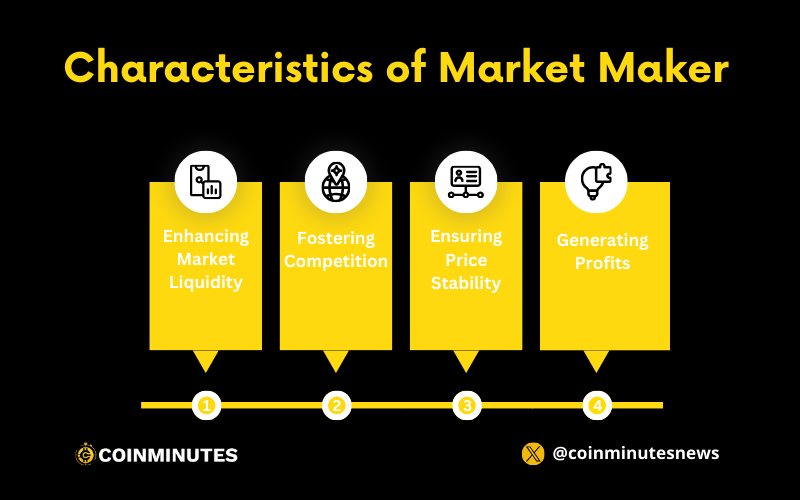
Characteristics and Roles of Market Maker
From the information provided about Market Makers earlier, we can derive some of their key characteristics and roles. Based on the following roles, it can be asserted that Market Makers are an essential component of the financial market.
Enhancing Market Liquidity:
- Market Makers play a vital role by consistently placing orders for both buying and selling in substantial volumes with narrow spreads. This approach facilitates the swift fulfillment of investors’ trade requests and encourages higher trading activity. With significant capital, Market Makers act as the ultimate buyer during low-demand periods and the ultimate seller when supply is abundant, thereby enhancing overall market liquidity.
Fostering Competition:
- Through the placement of orders at various price points, Market Makers contribute to the expansion of market depth. This, in turn, attracts a diverse range of investors, promoting healthy competition among orders within the market.
Ensuring Price Stability:
- In the face of pronounced price fluctuations, Market Makers adjust supply and demand dynamics to mitigate extreme price swings. This proactive stance helps in maintaining a stable price trend for the respective asset.
Generating Profits:
- As Market Makers, profits are realized by capitalizing on the price differentials when executing transactions as intermediaries. Buying at lower prices and selling at higher prices creates a profit margin for Market Makers.
Characteristics of Market Maker
Why Are Market Makers Important?
The primary responsibility of market makers is to uphold the functionality of financial markets by ensuring liquidity. They achieve this by placing substantial volumes of both buy and sell orders, facilitating smooth and convenient trading experiences.
In the absence of a market maker, selling securities can become challenging for investors as there may not always be readily available buyers in the market. In such situations, market makers step in as the “buyer of last resort” when a bondholder wishes to sell a security. Conversely, when an investor seeks to purchase a stock, the Market Maker assumes the role of the “seller of last resort.” Consequently, market makers function as wholesalers within financial markets.
Market Maker vs. Automated Market Maker
In general, both Market Maker and Automated Market Maker play an important market maker role, maintaining liquidity by simultaneously placing buy and sell orders, helping transactions execute seamlessly, and responding promptly. investor needs. Besides, there are still some differences below:
| Criteria | Automated Market Maker | Market Maker |
| Operations | Based on automatic algorithms, without direct human intervention | Based on a team of traders who monitor and intervene in the market |
| Order placing mechanism | Automatically places orders based on market conditions and predefined formulas | Based on traders’ experience and analysis |
| Transaction cost | Higher due to additional network fees on ETH | Lower |
| Accessibility | Easily accessible to all users, no KYC required | KYC required |
| Risk | Higher risk of impermanent loss when the market fluctuates strongly | Lower risk |
| Tradable assets | Support more types of assets including illiquid assets | Limited to highly liquid assets |
| Derivatives, margin products | Not fully developed | Fully developed |






